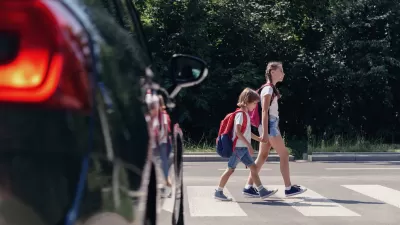A new report concludes that common ‘walkability’ measures don’t account for many barriers faced by pedestrians, such as environmental factors and policing.

According to Kea Wilson, “if cities truly want to be pedestrian-friendly, they need to think beyond the sidewalk, particularly in neighborhoods of color that face the steepest barriers.” However, while walkability scoring tools attempt to quantify the accessibility of neighborhoods for pedestrians, they leave out important factors. “That’s mostly because walkability algorithms tend to grade neighborhoods highly when they offer a lot of destinations within ‘walking distance,‘ but don’t closely scrutinize things like pedestrian crash rates, how long it takes to cross the road, the presence or absence of sidewalks, or even whether or not people you know, actually walk in a given neighborhood right now.”
A new analysis from the Urban Institute used five criteria to get a more accurate picture of actual walkability in Washington, D.C.: access to “essential destinations,” environmental quality factors such as air pollution and shade, infrastructure, policing, and road safety. “The study focused on data that could be sourced from public sources in hopes that other cities could easily replicate their work, but the researchers were forced to leave out certain critical and under-studied walking barriers, like rates of gender-based street harassment, accessibility for people with disabilities, and flood patterns in communities with poor drainage.”
“Still, the researchers say that’s all the more reason for city leaders to expand the kinds of data they collect on mobility barriers among various groups — and to think just as broadly about how improving one metric, like the prevalence of ‘self-enforcing’ street designs, could possibly improve other metrics, like decreasing the number of police stops.”
FULL STORY: Why ‘Walkability’ Scores Don’t Tell Us How Pedestrian-Friendly a City Is For Everyone

Alabama: Trump Terminates Settlements for Black Communities Harmed By Raw Sewage
Trump deemed the landmark civil rights agreement “illegal DEI and environmental justice policy.”

Planetizen Federal Action Tracker
A weekly monitor of how Trump’s orders and actions are impacting planners and planning in America.

Why Should We Subsidize Public Transportation?
Many public transit agencies face financial stress due to rising costs, declining fare revenue, and declining subsidies. Transit advocates must provide a strong business case for increasing public transit funding.

Understanding Road Diets
An explainer from Momentum highlights the advantages of reducing vehicle lanes in favor of more bike, transit, and pedestrian infrastructure.

New California Law Regulates Warehouse Pollution
A new law tightens building and emissions regulations for large distribution warehouses to mitigate air pollution and traffic in surrounding communities.

Phoenix Announces Opening Date for Light Rail Extension
The South Central extension will connect South Phoenix to downtown and other major hubs starting on June 7.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Caltrans
Smith Gee Studio
Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS)
City of Grandview
Harvard GSD Executive Education
Toledo-Lucas County Plan Commissions
Salt Lake City
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service