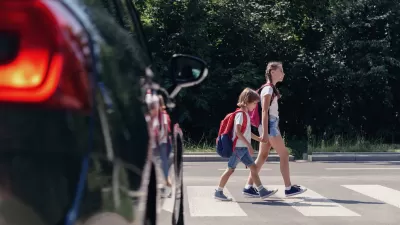Signs and markings designed for traffic control can make conditions less safe for pedestrians and other road users.

Writing in Streetsblog, Kea Wilson explains how the regulations codified in the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) can make roads less safe.
“Since the very first center line appeared on a Michigan road in 1911, many have questioned whether the design norms that govern the U.S. transportation network really make roads ‘safe,’ or simply less dangerous than the anarchic days of early motordom — though they're still nowhere near as safe as the days before the car dominated American roads at all.”
As transportation engineer Ian Lockwood explains, “The [signs, signals and markings in the] MUTCD aren't there to make our streets safer … They’re there to make them faster.” Signs and markings are designed to speed up traffic, and are less necessary at slower speeds. Cities that have experimented with removing signage and markings have seen positive results. “In 2016, transportation engineers in London found that when they removed center lines from several 30 mile-per-hour roads, traffic speeds and potential crash severity plummeted — perhaps validating Lockwood's hypothesis that the yellow line deserves some of the blame for traffic violence on U.S. roads, too.”
The concept known as Shared Space was pioneered by Dutch traffic engineer Hans Monderman, “who famously — if counter-intuitively — advised communities throughout Europe and Australia facing safety challenges to remove streetlights, lane markers, and even crosswalks, rather than following conventional wisdom that would have them install even more of them.” Lockwood adds that a misplaced faith in technology can cause people to behave less cautiously. “The lower tech we go, the more we have to drive responsibly.”
Despite proven increases in actual safety, pedestrians can perceive Shared Space interventions as making streets less safe. Removing physical curbs can also impede mobility for people with visual impairments who use curbs to identify where the sidewalk ends, for example.
But the ideology behind Shared Space—the belief that roads should be safe for all people—can be a useful approach for shifting focus away from trying to influence driver behavior with signage and designing safer roadways in the first place.
FULL STORY: Counter-Intuitive Department: Sometimes, Traffic Controls Make Streets More Dangerous

Manufactured Crisis: Losing the Nation’s Largest Source of Unsubsidized Affordable Housing
Manufactured housing communities have long been an affordable housing option for millions of people living in the U.S., but that affordability is disappearing rapidly. How did we get here?

Americans May Be Stuck — But Why?
Americans are moving a lot less than they once did, and that is a problem. While Yoni Applebaum, in his highly-publicized article Stuck, gets the reasons badly wrong, it's still important to ask: why are we moving so much less than before?

Using Old Oil and Gas Wells for Green Energy Storage
Penn State researchers have found that repurposing abandoned oil and gas wells for geothermal-assisted compressed-air energy storage can boost efficiency, reduce environmental risks, and support clean energy and job transitions.

Updating LA’s Tree Rules Could Bring More Shade to Underserved Neighborhoods
A new USC study finds that relaxing Los Angeles’ outdated tree planting guidelines could significantly expand urban tree canopy and reduce shade disparities in lower-income neighborhoods, though infrastructure investments are also needed.

California's Canal Solar Projects Aim to Conserve Resources and Expand Clean Energy
California’s Project Nexus has begun generating electricity from solar panels installed over irrigation canals, with researchers and state agencies exploring statewide expansion to conserve water and boost clean energy production.

HHS Staff Cuts Gut Energy Assistance Program
The full staff of a federal program that distributes heating and cooling assistance for low-income families was laid off, jeopardizing the program’s operations.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Heyer Gruel & Associates PA
City of Moreno Valley
Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS)
City of Grandview
Harvard GSD Executive Education
Salt Lake City
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service
City of Cambridge, Maryland