Massachusetts Department of Transportation plans to heighten and widen the Allston section of I-90 viaduct do not align with the community's desire for an environmentally friendly and pedestrian- and cycling-oriented new solution.
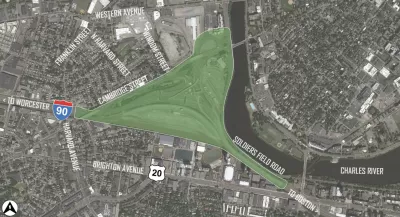
The Allston section of I-90, a stretch of viaduct wedged between Boston University and the Charles River, was opened 55 years ago. The highway constitution project bisected a lower-income community and damaged riverfront habitat. Boston, Brookline, and Cambridge are still paying the price for what Bradley Campbell and Richard Dimino call "failed transportation policy that placed a highway above the needs of neighborhoods and the environment."
Now the viaduct needs to be replaced. "Nearly all stakeholders, including the city of Boston, agree that we should pursue a strategy for I-90 that plans for our future transportation needs, not reprise last-century’s failed approaches to create a new, bigger viaduct," write Campbell and Dimino.
Still, MassDOT's “Modified Highway Viaduct” option takes that very approach, heightening and widening the viaduct.
Campbell and Dimino stress that better options exist. A Better City, led by Dimino, has proposed an at-grade design that adds trees and a living shoreline to the pedestrian and bike access space running along the river. "This improved surface option is also designed to ensure that two-track commuter rail service on the Worcester Line remains in service during construction," they say.
Governor Charlie Barker should step up and give "Boston and the region a western gateway equal to its aspirations as a leader in urban design, transportation vision, and environmental planning," Campbell and Dimino assert.
FULL STORY: A new, bigger I-90 viaduct is not the answer

Study: Maui’s Plan to Convert Vacation Rentals to Long-Term Housing Could Cause Nearly $1 Billion Economic Loss
The plan would reduce visitor accommodation by 25,% resulting in 1,900 jobs lost.

North Texas Transit Leaders Tout Benefits of TOD for Growing Region
At a summit focused on transit-oriented development, policymakers discussed how North Texas’ expanded light rail system can serve as a tool for economic growth.

Using Old Oil and Gas Wells for Green Energy Storage
Penn State researchers have found that repurposing abandoned oil and gas wells for geothermal-assisted compressed-air energy storage can boost efficiency, reduce environmental risks, and support clean energy and job transitions.

Private Donations Propel Early Restoration of Palisades Playground
Los Angeles has secured over $1.3 million in private funding to restore the Pacific Palisades playground months ahead of schedule, creating a modern, accessible space that supports community healing after recent wildfires.

From Blight to Benefit: Early Results From California’s Equitable Cleanup Program
The Equitable Community Revitalization Grant (ECRG) program is reshaping brownfield redevelopment by prioritizing projects in low-income and environmental justice communities, emphasizing equity, transparency, and community benefits.

Planting Relief: Tackling Las Vegas Heat One Tree at a Time
Nevada Plants, a Las Vegas-based nonprofit, is combating the city’s extreme urban heat by giving away trees to residents in underserved neighborhoods, promoting shade, sustainability, and community health.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Ascent Environmental
Borough of Carlisle
Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS)
City of Grandview
Harvard GSD Executive Education
Toledo-Lucas County Plan Commissions
Salt Lake City
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service




























