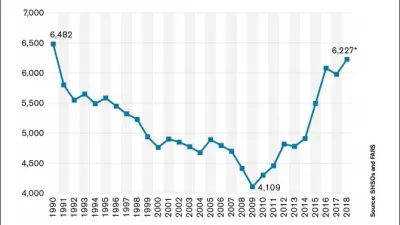
Pedestrian deaths are on the rise in the United States, but cities have been slow to implement effective policies and road design measures to change the trend.

While the number of pedestrian deaths has been dropping in other countries, the United States is projected to reach a high not seen in 30 years, reports a team from the Howard Center for Investigative Journalism at Arizona State University.
Drivers are safer than ever in vehicles outfitted with a number of features to better protect them. However, experts do not agree on the causes behind the increase in pedestrian fatalities. They point to distracted driving and an increase in walking, but these factors do not adequately explain the trends seen here in the United States and other countries.
And a closer look at the data indicates that certain places have been disproportionately affected. "The threat posed by vehicles is exacerbated by road designs in many of the country’s most dangerous locations for pedestrians — mostly low-income, predominantly minority neighborhoods in heavily populated Sun Belt cities, such as Los Angeles, Phoenix, Houston and Orlando, Fla."
Arterial roads in these areas are wide with high traffic volumes and speeds. "Many of these roads, which are designed for vehicle speeds of over 40 mph, are hostile to pedestrians. They have sidewalks that abut the travel lanes with minimal separation and lack median islands or sufficient lighting."
Some cities have adopted Vision Zero initiatives to address road safety, but others—such as Phoenix, which has one of the highest pedestrian fatality rates in the country—have fully rejected such strategies. In addition, the European Union has adopted vehicle safety standards to better protect pedestrians, but the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration says such regulations did not pass a required cost-benefit analysis.
FULL STORY: Pedestrians die every 90 minutes in the U.S., and low-income areas are hurt most

Study: Maui’s Plan to Convert Vacation Rentals to Long-Term Housing Could Cause Nearly $1 Billion Economic Loss
The plan would reduce visitor accommodation by 25,% resulting in 1,900 jobs lost.

North Texas Transit Leaders Tout Benefits of TOD for Growing Region
At a summit focused on transit-oriented development, policymakers discussed how North Texas’ expanded light rail system can serve as a tool for economic growth.

Using Old Oil and Gas Wells for Green Energy Storage
Penn State researchers have found that repurposing abandoned oil and gas wells for geothermal-assisted compressed-air energy storage can boost efficiency, reduce environmental risks, and support clean energy and job transitions.

Private Donations Propel Early Restoration of Palisades Playground
Los Angeles has secured over $1.3 million in private funding to restore the Pacific Palisades playground months ahead of schedule, creating a modern, accessible space that supports community healing after recent wildfires.

From Blight to Benefit: Early Results From California’s Equitable Cleanup Program
The Equitable Community Revitalization Grant (ECRG) program is reshaping brownfield redevelopment by prioritizing projects in low-income and environmental justice communities, emphasizing equity, transparency, and community benefits.

Planting Relief: Tackling Las Vegas Heat One Tree at a Time
Nevada Plants, a Las Vegas-based nonprofit, is combating the city’s extreme urban heat by giving away trees to residents in underserved neighborhoods, promoting shade, sustainability, and community health.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Ascent Environmental
Borough of Carlisle
Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS)
City of Grandview
Harvard GSD Executive Education
Toledo-Lucas County Plan Commissions
Salt Lake City
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service