Communities have good reasons to protect trees and forests. Planners can help make this happen.

Last week was Tu Bishvat, the Jewish new year of the trees, when we celebrate trees and all of the great things they provide. Hug a tree, visit a forest, and enjoy fruits! Everybody is welcome: Judeo-Christians, pagans, Shintoists, rational humanistic environmentalists, and other beings, all have good reasons to celebrate, appreciate, and protect trees.
Communities have many good reasons to protect trees and forests, or to use the more general terms, green space and open space, which includes parks, farms and natural habitat. Urban green space makes people healthier and happier, reduces stormwater management costs, and reduces heat island effects. Preserving wildlife habitat is critical to a healthy global ecosystem. Impervious surface area (land covered by buildings, pavement and other hard surfaces) can be considered a key environmental indicator: as impervious surface increases environmental quality declines.

What does this mean for planning? Many public policies and planning decisions affect urban trees, open space, and pavement. The following practices can help minimize per capita impervious surface area and preserve environmentally healthy lands.
Local governments can plant trees, for example, along streets, which provide beauty, shade, habitat, and air quality, and as much as possible, favor native varieties that support local ecosystems. Governments can also encourage private property owners to plant trees and other natural habitat, and minimize monoculture lawns, which are the least productive type of green space. They can debunk anti-tree myths, such as claims that lower-income neighborhoods don't value tree-cover or that trees harm infrastructure such as sidewalks and utility lines.

Governments can also plan for adequate public parks. For health and happiness, urban households should be located within a ten minute walk of local parks and recreational facilities, and 20% or more of urban land should be devoted to public parks.
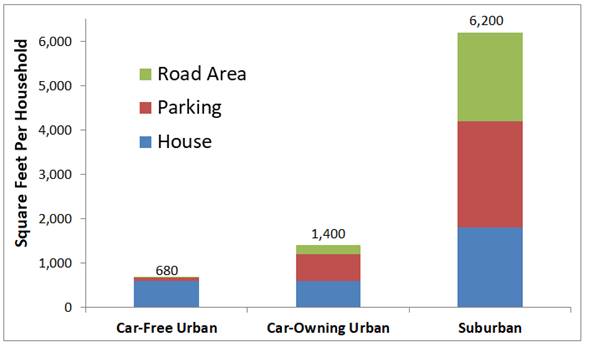
However, urban tree preservation should not be an impediment to compact infill development. As discussed in one of my previous blogs, "Seeing the Urban Forest for the Trees," infill projects often require displacing trees, which NIMBYs use to oppose those projects, resulting in far larger environmental damages from more lower-density, sprawled development. Considering house, road, and parking requirements, a typical household living car-free in an urban townhouse or apartment requires just a tenth as much impervious surface as the same family with two cars living in a single-family suburban house.
Roadway planning decisions often involve trade-offs between trees and traffic or parking capacity. Many communities are applying streescaping and road diet concepts to reduce the amount of road right-of-way that must be devoted to pavement to accommodate more green space. In the past, trees along roadways were often removed to safely accommodate higher speed traffic; a new ethos preserves trees and reduces traffic speeds for safety and livability sake.
Regional governments can encourage compact infill over urban expansion with Smart Growth and New Urbanist policies that increase allowable densities and building heights, establish urban growth boundaries, and by reducing subsidies that encourage sprawled development, such as urban fringe utility line and roadway expansions. This provides many economic, social and environmental benefits.
In urban areas, a major portion of impervious surface consists of roads and parking facilities. Surveys indicate that typical communities have two to six off-street parking spaces per vehicle, plus significant amounts of land devoted to highways. Reducing vehicle ownership and managing parking facilities more efficiently so fewer spaces are needed to serve motorists' demands, helps free up urban land for more affordable housing and green space.
Most fundamentally, planners can help their communities implement more multimodal transportation planning and establish vehicle-travel reduction targets to favor space-efficient modes (e.g., walking, bicycling, and public transit) over space-intensive automobile travel.

Life is better with trees! Smart planning can protect greenspace for a better quality of life, infrastructure savings, and environmental protection.
For More information
American Forests provides tools for tree and forest protection.
Subha Ranjan Banerjee and Ben Welle (2016), Bigger Isn’t Always Better: Narrow Traffic Lanes Make Cities Safer, World Resources Institute.
CNT (2016), Stalled Out: How Empty Parking Spaces Diminish Neighborhood Affordability, Center for Neighborhood Technology.
GreenTRIP Connect is a free tool allowing users to easily calculate how accessible, multi-modal location and traffic reduction strategies can reduce driving from residential development throughout California, and calculates how much money and space can be saved from right-sized parking.
Todd Litman (2016), Parking Management: Comprehensive Implementation Guide, Victoria Transport Policy Institute.
Reinventing Parking is a website the provides ideas for parking policy reforms.
Ottawa (2015), A 90 Second Lesson in How Parking Can Kill Cities, City of Ottawa.
Richard Willson (2015), Parking Management for Smart Growth, Island Press.

Alabama: Trump Terminates Settlements for Black Communities Harmed By Raw Sewage
Trump deemed the landmark civil rights agreement “illegal DEI and environmental justice policy.”

Study: Maui’s Plan to Convert Vacation Rentals to Long-Term Housing Could Cause Nearly $1 Billion Economic Loss
The plan would reduce visitor accommodation by 25% resulting in 1,900 jobs lost.

Planetizen Federal Action Tracker
A weekly monitor of how Trump’s orders and actions are impacting planners and planning in America.

Wind Energy on the Rise Despite Federal Policy Reversal
The Trump administration is revoking federal support for renewable energy, but demand for new projects continues unabated.

Passengers Flock to Caltrain After Electrification
The new electric trains are running faster and more reliably, leading to strong ridership growth on the Bay Area rail system.

Texas Churches Rally Behind ‘Yes in God’s Back Yard’ Legislation
Religious leaders want the state to reduce zoning regulations to streamline leasing church-owned land to housing developers.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Caltrans
Smith Gee Studio
Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS)
City of Grandview
Harvard GSD Executive Education
Toledo-Lucas County Plan Commissions
Salt Lake City
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service






























