Yuan Man guest blogs about a recent article in the Journal of Planning Education and Research.

What is the relationship between urban planning and air quality in China? Rapid growth and greatly expanded motor vehicle ownership and usage have contributed to serious air pollution across China. In 2013, 96 percent of key cities did not meet the national ambient air quality standard. In 2014 alone, Beijing endured more than 20 days with almost ten times the national ambient air quality limit, causing public health issues. Scholars from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill recently published a paper in the Journal of Planning Education and Research evaluating this question.
Based on evidence gathered from 157 Chinese cities, the study analyzed the effects of aspects of urban form metrics on concentrations of ambient pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, CO, and O3). Six urban form metrics were calculated using data from nighttime light images, land use, LandScan population, Baidu points of interest (POI) and others sources. These are population density, degree of centering, land use mix, street accessibility, shape complexity, and urban continuity. Linear regressions were used to evaluate the effects of urban form metrics on concentrations of six air pollutants after controlling for socioeconomic factors such as GDP, industrial emissions and meteorology.
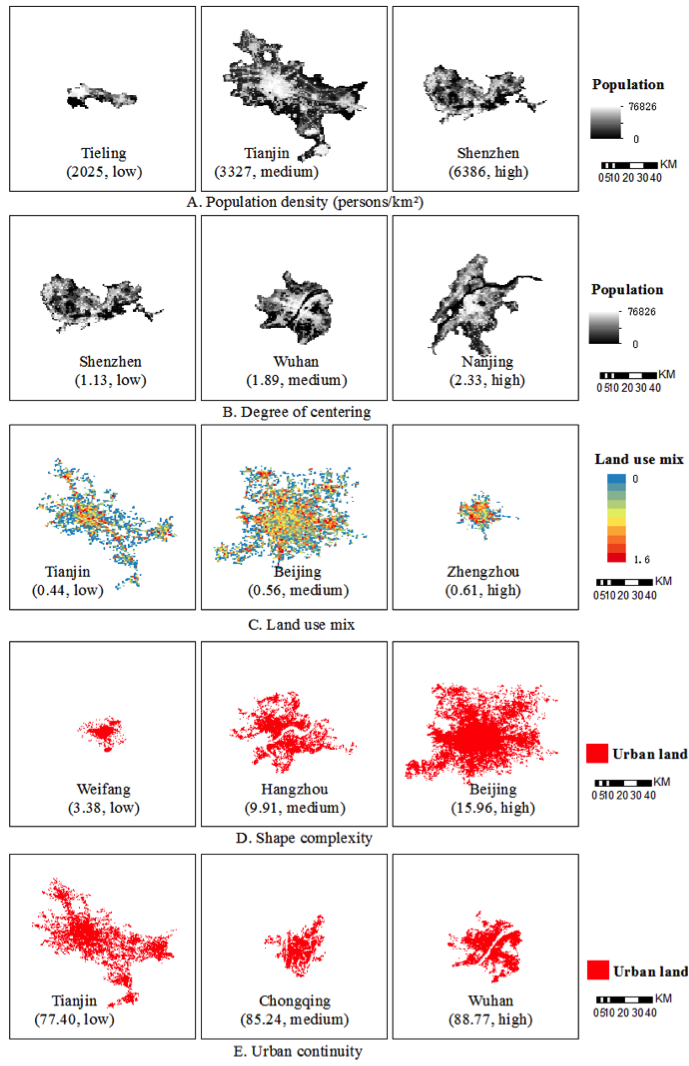
The study finds that greater population density, more centralized development and better street accessibility have a significant correlation with lower concentrations of air pollutants, and that higher levels of urban sprawl may have a negative impact on air quality. Population density is negatively associated with concentrations of PM2.5, PM10 and O3, because higher densities may reduce per capita emission by decreasing automobile dependence and travelling distance. More centering and subcentering in urban areas help to improve air quality, because less centralized development may increase travelling distances between urban centers and different destinations. Better street accessibility could reduce traffic congestions and increase vehicle speeds, thus reducing vehicle emissions. Higher urban continuity is associated with higher concentrations of air pollutants, which may be caused by non-emission-based mechanisms such as urban heat island effect or pollutant dispersion.
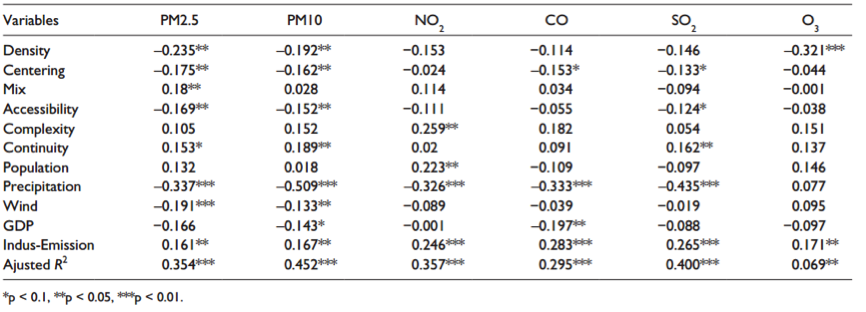
“The influence of urban form on pollution,” write the authors, “is comparable to the effects of other factors like weather conditions.” Although population densities of Chinese cities are much higher than American cities, urban sprawl is becoming increasing common in China. Cities with urban sprawl are more likely to contain higher levels of air pollution, which should draw wide attention from local governments and planners in China. “These findings indicate that urban form could play a modest, but important, role in improving air quality for Chinese cities.” Lessons from Chinese cities could provide some implications for urban planning in developing countries.
Open Access Until December 7th, 2017

Trump Administration Could Effectively End Housing Voucher Program
Federal officials are eyeing major cuts to the Section 8 program that helps millions of low-income households pay rent.

Planetizen Federal Action Tracker
A weekly monitor of how Trump’s orders and actions are impacting planners and planning in America.

Ken Jennings Launches Transit Web Series
The Jeopardy champ wants you to ride public transit.

Rebuilding Smarter: How LA County Is Guiding Fire-Ravaged Communities Toward Resilience
Los Angeles County is leading a coordinated effort to help fire-impacted communities rebuild with resilience by providing recovery resources, promoting fire-wise design, and aligning reconstruction with broader sustainability and climate goals.

When Borders Blur: Regional Collaboration in Action
As regional challenges outgrow city boundaries, “When Borders Blur” explores how cross-jurisdictional collaboration can drive smarter, more resilient urban planning, sharing real-world lessons from thriving partnerships across North America.

Philadelphia Is Expanding its Network of Roundabouts
Roundabouts are widely shown to decrease traffic speed, reduce congestion, and improve efficiency.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
Ada County Highway District
Clanton & Associates, Inc.
Jessamine County Fiscal Court
Institute for Housing and Urban Development Studies (IHS)
City of Grandview
Harvard GSD Executive Education
Toledo-Lucas County Plan Commissions
Salt Lake City
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service






























